Binary Search
The Binary Search algorithm is a highly efficient searching algorithm used to find a target element in a sorted collection by repeatedly dividing the search interval in half.
Algorithm Overview
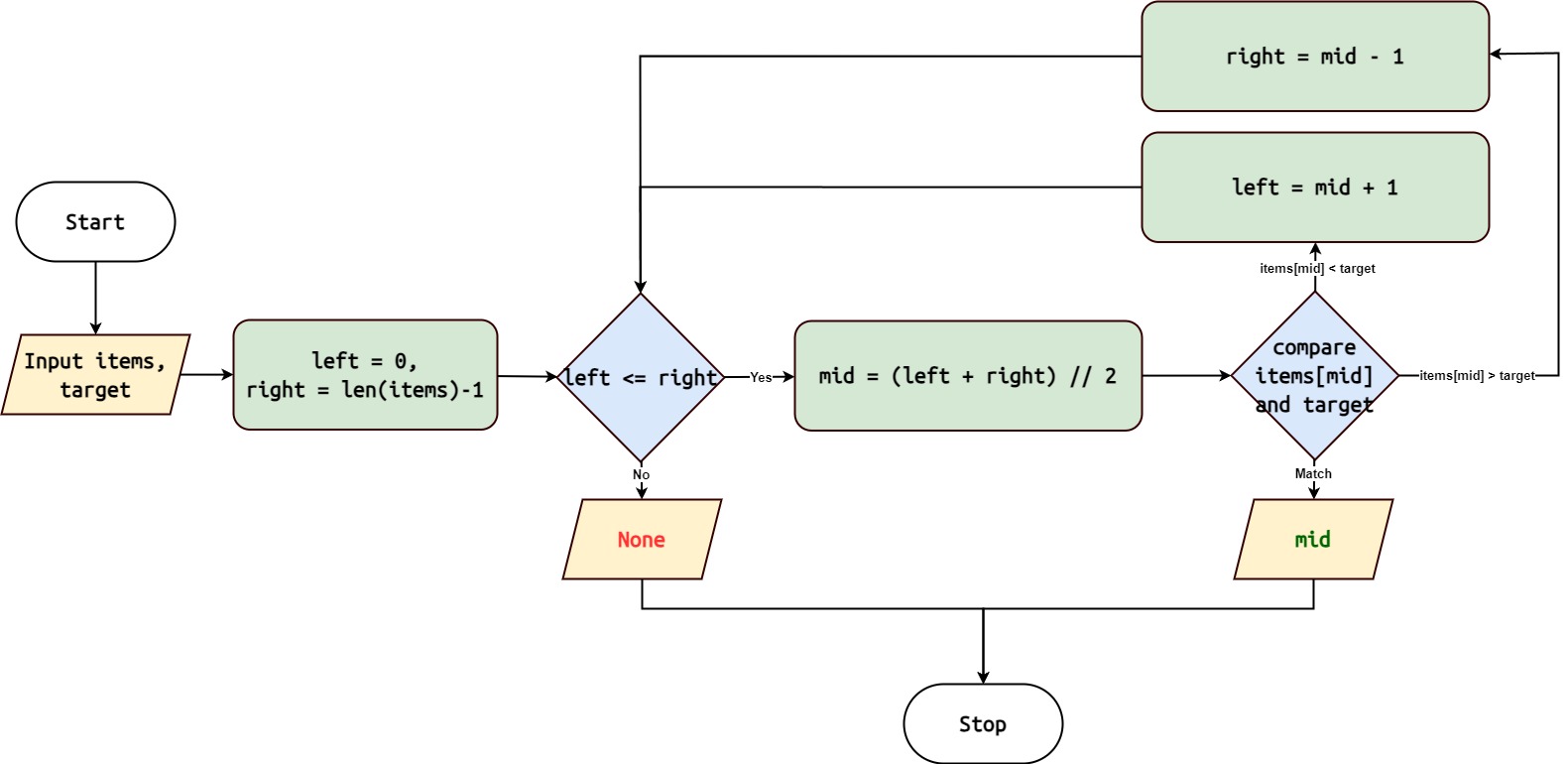
Initialize two pointers, left and right, representing the leftmost and rightmost indices of the collection, respectively.
While the left pointer is less than or equal to the right pointer:
Calculate the middle index as (left + right) // 2.
If the middle element is equal to the target element, return its index.
If the middle element is greater than the target element, update the right pointer to mid - 1.
If the middle element is less than the target element, update the left pointer to mid + 1.
If the target element is not found after the loop, return None.
Note
Binary Search requires the collection to be sorted and has a time complexity of O(log n), where ‘n’ is the number of elements in the collection.
Implementation in Python
Here’s a Python implementation of the Binary Search algorithm:
1 def binary_search(target: Any, items: List[Any]) -> Optional[int]:
2 left, right = 0, len(items) - 1
3 while left <= right:
4 mid = (left + right) // 2
5 if items[mid] == target:
6 return mid
7 elif items[mid] < target:
8 left = mid + 1
9 else:
10 right = mid - 1
11 return None
Usage
To use the binary_search function:
1 from algorithms import binary_search
2
3
4 arr = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
5 target = 5
6 index = binary_search(target, arr)
7 if index is not None:
8 print(f"Element {target} found at index {index}")
9 else:
10 print(f"Element {target} not found")